Easily plan, deploy, provision, and maintain SLA-based business services over any access: fiber/copper/TDM/mobile, with Carrier Ethernet access and aggregation supporting rates up to 1/10/25/100G/400G*. Solution for business class access to internet, cloud and VPN services.
5G Network Technology Use Cases
5G Solutions
Since 5G technology began its commercial use in 2019, it was clear that it isn’t just another mobile technology like its predecessors. While 4G/LTE had been – and still is – used for more than smart phone connectivity, 5G, with its ultra-high bandwidth, minimal delay and unique architecture, represents a clear departure from past practices with new use cases in the realms of business communications, industrial campuses and asset management IoT deployments. These new 5G use cases are discussed below, together with their specific requirements and the relevant RAD’s 5G solutions that address them.
5G Slicing
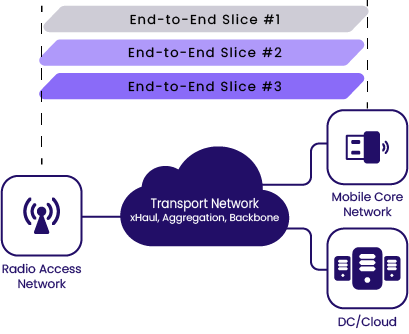
One of 5G’s compelling innovations is Slicing: A key mechanism of 5G networks that allows using shared networks for multiple services with different attributes such as bandwidth, delay requirements, required functionality, etc. In this context, a network slice is a logical network that provides specific capabilities and characteristics. In some networks, there may be a huge number of slice instances in order to isolate individual user flows.
A key requirement to achieve this is to ensure an end-to-end network slicing support, not only in the radio access network (RAN) but also in the transport segment.
Ethernet Business Services and Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) over 5G
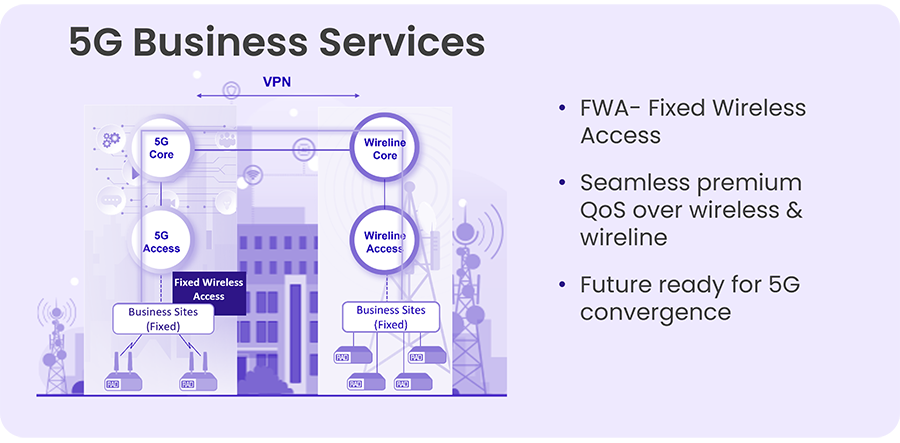
Ethernet Business Services over 5G enable service providers to deliver carrier-grade connectivity using Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) instead of traditional fiber. By leveraging 5G networks, CSPs can extend Ethernet services—such as E-Line, E-LAN, and E-Access—to enterprise and industrial sites where laying fiber is impractical, time-consuming, or too expensive. This approach supports MEF-compliant Layer 2 services with SLA-grade performance, bringing flexibility and reach to network operators and their business customers.
Ethernet Business Services over 5G enable service providers to deliver carrier-grade connectivity using Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) instead of traditional fiber. By leveraging 5G networks, CSPs can extend Ethernet services—such as E-Line, E-LAN, and E-Access—to enterprise and industrial sites where laying fiber is impractical, time-consuming, or too expensive. This approach supports MEF-compliant Layer 2 services with SLA-grade performance, bringing flexibility and reach to network operators and their business customers.
As digitalization accelerates, businesses are generating more data than ever. Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) over 5G allows organizations to deploy high-performance backhaul in places where fiber isn’t feasible, bridging the gap between performance needs and deployment agility.
The typical architecture includes a 5G cellular gateway installed at the customer site, connected via 5G New Radio to either public or private 5G infrastructure. These gateways are equipped with all service delivery and demarcation capabilities to allow the CSP to meet its SLA guarantees. In addition, dual-SIM failover adds service resilience, which is also expected by the business customer. Traffic is transported over 5G to an edge aggregation point or cloud-hosted gateway, where it is handed off to the service provider’s core network. Service lifecycle management such as provisioning, monitoring, and SLA enforcement is handled by the management system, such as RADview, ensuring end-to-end performance visibility and control.
Given that 5G traffic is typically IP/L3 based, service providers can choose between two alternatives to transport Ethernet/L2 traffic over it: Encapsulation and tunneling in standalone (SA) or non-standalone (NSA) 5G modes, or using 5G native L2 PDU transport (in SA deployments only), since the latter allows simpler transport, it is increasingly gaining traction among 5G vendors and operators.
This approach is ideal for a variety of use cases. Service providers can offer reliable backup connectivity for enterprise customers, extending business services to remote or underserved areas without the need for fiber. It supports both permanent and temporary deployments—such as construction sites, events, or mobile offices
The value for CSPs is substantial: it closes the coverage gap and provides instant connectivity to business sites; it solves coverage issues in underground locations at a lower cost than fiber; and it allows providers to generate revenues from their current 5G infrastructure.
In short, Ethernet over 5G with FWA unlocks new revenue streams, faster service delivery, and greater flexibility for both providers and enterprise users—backed by RAD’s proven technology stack.
Private 5G
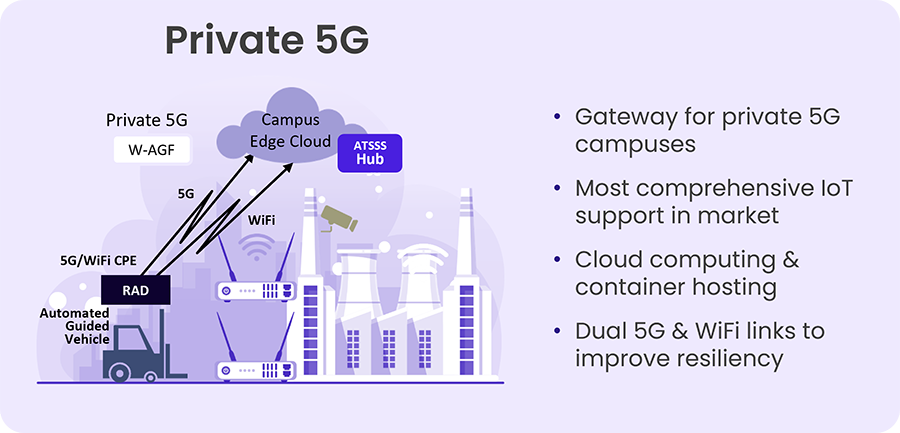
Private networks offer valuable benefits to some users, such as enterprises, utilities and other organizations that run their operations within a campus. Unlike public networks that share multiple users, private networks are designed for an organization’s specific needs and are dedicated only to this user’s traffic. The increased control and security, as well as the tailored performance this provides, have made private 4G/LTE and now Private 5G networks increasingly popular. Private 5G offers high-performance wireless environments which enable companies to meet the demands for low latency, high bandwidth, and most of all uninterrupted connectivity.
The frequency bands used for Private 5G networks are different from those utilized for public 5G. To serve a broad customer base and ensure large coverage, public 5G networks – primarily operated by mobile carriers – typically use licensed spectrum. Private 5G networks, on the other hand, require an optimized fit for specific use cases by the organization or enterprise that operate them. To achieve that, they can utilize either unlicensed spectrum, licensed spectrum, such as the 900 MHz used by Anterix in N. America, or shared spectrum such as CBRS.
The biggest challenge for organizations operating private campus networks is the need to maintain reliable connectivity within the private network and to the cloud. Within the network, it is common for connected devices of various generations to co-exist, all required to be onboarded onto the network and connected to the central IoT management system. Cyber risks have also increased exponentially with the growing connectedness, which also requires addressing.
RAD’s Solution for Private 5G Networks
RAD enables flexible, ultra-resilient connectivity to the cloud over 5G networks using a robust IoT gateway that ensures uninterrupted data delivery. Within the private 5G network, the IoT gateway supports flexible communication for smart devices using LoRaWAN, Wi-Fi HaLow, serial, and Ethernet links. In addition to scalable and reliable connectivity, RAD’s solution provides enhanced security and seamless integration with legacy systems.
Furthermore, in 5G campuses that also utilize WiFi indoors, RAD’s solution delivers uninterrupted service with seamless traffic split between WiFi and 5G , traffic switchover to 5G due to WiFi cut-off and traffic switchback to multi-path WiFi and 5G.
5G xHaul for Mobile Networks
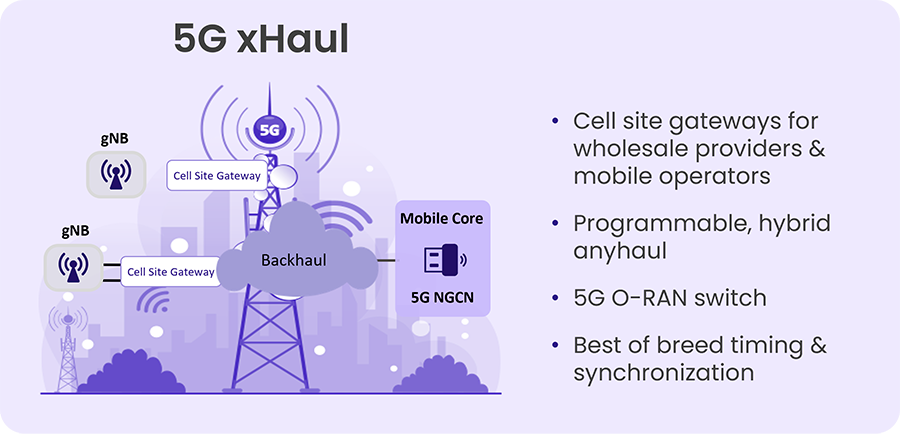
Prior to the emerging use cases in enterprise, utilities and industrial markets, 5G originated as a mobile technology, albeit being a revolutionary one compared to earlier generations. For mobile services, the 5G RAN breaks down the base station – gNB – into three separate entities: Radio unit (RU), a distributed unit (DU) and a central unit (CU). The transport segment between a remote RU and the rest of the gNB is called fronthaul. If the CU is physically detached from the DU, the transport segment between them is termed midhaul. The connection between the gNB and the core network is called backhaul. These segments are collectively termed “5G xHaul ”.
While the 3GPP, the standardization body responsible for the 5G standards, deals in minute detail with all aspects of the connection between the user equipment (e.g., a smartphone) and the gNB, and the connection between the gNB and the 5G core, the connections inside the RAN and to the core are viewed as ideal transport pipes. Transport is considered as a trivial function that effortlessly delivers data over the named interfaces with no availability failures, data-rate restrictions, burdensome latency, synchronization glitches, or other degradations.
Unfortunately, even well-engineered transport networks have limitations and occasionally fail to live up to design requirements.
RAD’s 5G xHaul Solution
RAD’s offers comprehensive support for 5G fronthaul, midhaul and backhaul using a single, economical cell site gateway (CSG):
MEF 22.3.1-certified supporting Transport for 5G Mobile Networks
Fits multi-RAT 4G/5G RANs
Supports various 5G RAN splits, including lower-level splits 8 and 7.2 with high bandwidth low latency requirements.
Provides highly efficient 4G/5G aggregation: 10G, 25G, 50G, and 100G, with timing synchronization
Solves operational complexity and cost issues where different platforms are used.
Enables future upgrades in the field to address new requirements without forklifts.
This allows fast rollouts of 5G deployments with in-field future upgrades to meet new requirements, as well as support for wholesale and direct MNO applications.