Your Network's Edge®
Demo Videos
You are here
Edge Computing in Industrial IoT with OpenPLC, SCADA Firewall Use Cases
Video #1: Edge Computing in Industrial IoT
Industrial IoT is a new and exciting trend that is aimed at increasing efficiency and lowering costs. This is achieved via cool technologies, like smart devices, or Things, and Big Data analytics. BUT, it also involves massive data transmissions – to and from many remote sites.
The big challenge is doing so over many different network connections.
Plus, there’s also the need for real-time analytics to get actionable information and make sense of all the data collected.
To solve these issues, the industry has come up with a smart approach that has become increasingly popular.
It’s called edge computing.
So what is edge computing, exactly?
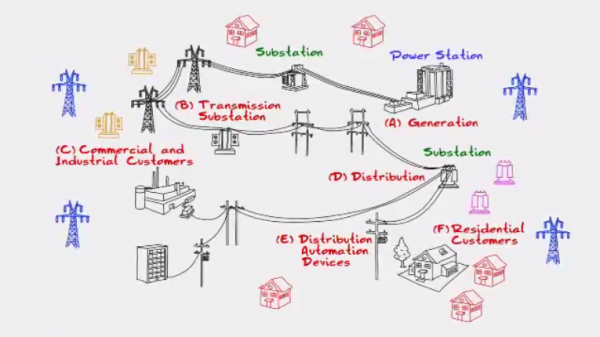
The most common view is a cloud environment, in which the storage and processing of data is performed closer to the edge of the network.
In other words, it is distributed, instead of being carried out at the data center.
The data itself is coming from automation-enabled devices.
These could be sensors, meter concentrators, or CCTV cameras, to name just a few.
What connects these devices to the operational network and control center is an industrial IoT gateway. And by adding cloud computing resources to the gateway, we get local storing and data processing at the edge.
This approach offers some impressive benefits, which is probably why it has become so popular.
- First, we get higher reliability since the data doesn’t need to travel to a central cloud, there is no risk of service interruption if the link is down
- This also enables lower delay in the network and consumes less resources compared to a centralized cloud deployment
- And last, but definitely not least, we can achieve better security since data isn’t traveling over public links.
Cloud computing and virtualization enable multiple applications to run independently on the same hardware at the same time. This means that a single Industrial IoT gateway can host networking and non-networking functions. By non-networking functions, we mean software-based customized applications for Industrial IoT management.
The end result is less “boxes” and better security. The function that needs to be secured is virtualized within the securely connected industrial IoT gateway itself. We can also add anomaly detection – both for cyber and networking functions.
The bottom line is that edge computing provides insight and agility, while reducing the number of devices in remote sites.
In our next installment, we’ll take a closer look at some interesting use cases for edge computing.
Video #2 – Industrial IoT Open PLC with Edge Computing
In a typical utility Field Area Network deployment, there are many remote sites with remote terminal units, also known as RTUs. RAD’s SecFlow is used to cyber-secure the data access to these devices. But the SecFlow does much more than handling secure networking. In fact, the controller or PLC software can be added to the SecFlow using edge-computing. SecFlow’s analog and digital inputs/outputs now make the external RTU redundant.
Here we see the Open PLC software with all its functionality within the SecFlow. The HMI user can remotely control all units in the field and adjust the operation of sensors and relays as necessary, bringing automation to the network.
Not only are the number of boxes reduced, but overall cyber security has also been improved significantly.
No one can physically access the RTU any longer as it is fully contained within the SecFlow.
With the increased awareness of the need for cyber security in automation environments, there are key industrial IoT applications that are meant to ensure data integrity and prevent unauthorized traffic from entering the system.
Let’s take a look at how edge computing can be used to secure industrial controllers, or PLCs. In this case, we’re adding SCADA Firewall functionality to the SecFlow. The SecFlow now monitors SCADA traffic between PLCs, and logs relevant activity. If necessary, it can also actively block traffic for intrusion prevention. What we’re seeing is the monitoring of DNP-3 traffic. Of course, Other SCADA protocols are also supported.
- Edge Computing in Industrial IoT with Open PLC Use Case
Watch the Video
- Edge Computing in Industrial IoT with SCADA Firewall Use Case
Watch the Video